Basemap is a great library for mapping faster than other python options, but there are some usual things I couldn't find how to do. Clipping a raster using a shape is one of them. Here's how do I do it
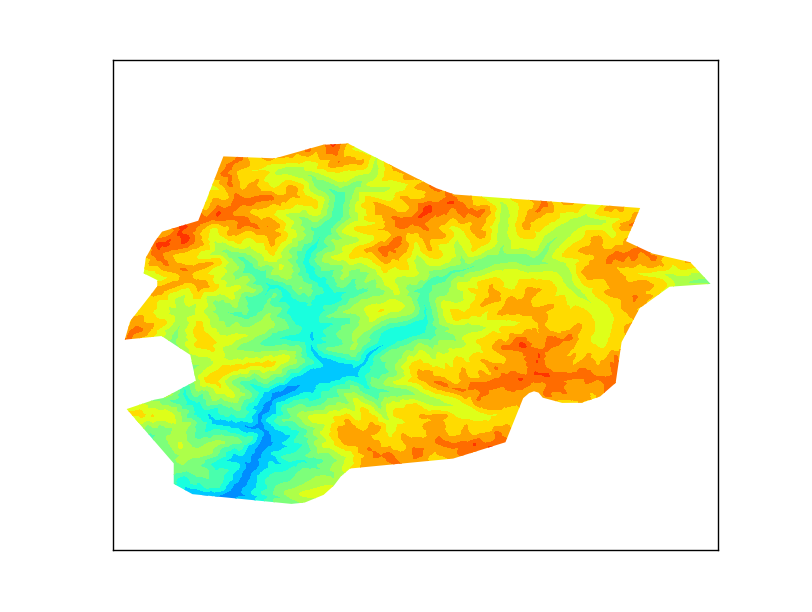 |
| The output |
As usual, all the code can be found at GitHub
Getting some data
The example plots some elevation data, taken from the SRTM. After looking for some options, the easiest to work with was this one: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/SELECTION/inputCoord.asp
The shapefile will be the border of Andorra, taken from Natural Earth
The result is a little poor because the resolution is low, but works well for the example.
The script
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
from matplotlib.path import Path
from matplotlib.patches import PathPatch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from osgeo import gdal
import numpy
import shapefile
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
sf = shapefile.Reader("ne_10m_admin_0_countries")
for shape_rec in sf.shapeRecords():
if shape_rec.record[3] == 'Andorra':
vertices = []
codes = []
pts = shape_rec.shape.points
prt = list(shape_rec.shape.parts) + [len(pts)]
for i in range(len(prt) - 1):
for j in range(prt[i], prt[i+1]):
vertices.append((pts[j][0], pts[j][1]))
codes += [Path.MOVETO]
codes += [Path.LINETO] * (prt[i+1] - prt[i] -2)
codes += [Path.CLOSEPOLY]
clip = Path(vertices, codes)
clip = PathPatch(clip, transform=ax.transData)
m = Basemap(llcrnrlon=1.4,
llcrnrlat=42.4,
urcrnrlon=1.77,
urcrnrlat=42.7,
resolution = None,
projection = 'cyl')
ds = gdal.Open('srtm_37_04.tif')
data = ds.ReadAsArray()
gt = ds.GetGeoTransform()
x = numpy.linspace(gt[0], gt[0] + gt[1] * data.shape[1], data.shape[1])
y = numpy.linspace(gt[3], gt[3] + gt[5] * data.shape[0], data.shape[0])
xx, yy = numpy.meshgrid(x, y)
cs = m.contourf(xx,yy,data,range(0, 3600, 200))
for contour in cs.collections:
contour.set_clip_path(clip)
plt.show()
- I used the pyshp library for reading the shapefile, since Fiona and GDAL don't work well together, and OGR was longer
- Lines 14 to 27 create the path. A Matplotlib path is made by two arrays. One with the points (called vertices in the script), and the other with the functions for every point (called codes)
- In our case, only straight lines have to be used, so there will be a MOVETO to indicate the beginning of the polygon, many LINETO to create the segments and one CLOSEPOLY for closing it
- Of course, only the polygon for Andorra has to be used. I get it from the shapefile attributes
- The prt array is for managing multipolygons, which is not the case, but the code will create correct clipping for multipolygons
- The path is created using the Path function, and then added to a PathPatch, to be able to use it as a closed polygon. Note the trasnform=ax.transData attribute. This assumes the polygon coordinates to be the ones used in the data (longitudes and latitudes in our case). More information here
- Next code lines draw the map as usual. I have used a latlon projection, so all the values for the raster and shapefile can be used directly. If the output raster was in an other projection, the shapefile coordinates should be appended to the path using the output projection (m(pts[j][0], pts[j][1]))
- The x and y coordinates are calculated from the GDAL geotransform, and then turned into a matrix using meshgrid
- The clipping itself is made in the lines 48 and 49. For each drawn element, the method set_clip_path is applied
Nice share! But have you tried other projection methods? I've tried Mercator projection method('Merc') and others but it didn't work. I don't know why. It seems that this solution only works for 'cyl' projection method.... Any solution for other projection method like Mercator?
ReplyDeleteHi, sorry for answering so late!
DeleteThe shapefile must be in lat lon projection (cyl, in basemap), but the final map, doesn't. To use it with other coordinates, the vertices should be reprojected into the map projection:
vertices = m(vertices)
Roger
Hi Roger,
DeleteThanks a lot. I've solved the problem. Now I still have a small question about the line " ax = fig.add_subplot(111) " at the beginning of the script. I wonder what "111" means here. Does it mean adding a subplot with the white color background(1,1,1)?
Shangxin
Hi Shangxin,
ReplyDeleteI wrote a tutorial which explains this:
http://basemaptutorial.readthedocs.org/en/latest/subplots.html
111 means that you are plotting a matrix of mps with one row and one column (the first two ones), and using the first one (the last one).
211 would be a map above the other, and plotting the upper one. 212, would plot the lower.
This comment has been removed by the author.
DeleteHi Roger,
DeleteThanks again. I got it! This is quite similar with Matlab's subplot definition. (1,1,1) would be more accessible than (111).
Shangxin
Yes, it's based on the matlab notation. Actually, using (1,1,1) is also possible, but many people uses it in my way, and I got used to it. Separating the arguments makes it easier to understand.
DeleteRoger
I am so happy after read your blog. It’s very useful blog for us.
ReplyDeletePython in-house training for employees in Nigeria
Wow, this guide on base map raster clipping with shapefiles is incredibly helpful! For those looking to enhance their image editing workflow, Graphic Experts India offers amazing clipping path services that perfectly complement projects like this.
ReplyDelete